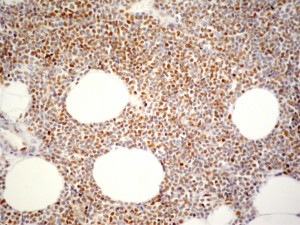
El reordenamiento del gen MYC es característico del linfoma de Burkitt y también está presente en el 10-15% de los linfomas difusos de célula grande (DLBCL) y en el 35-50% de los linfomas B con características intermedias entre Burkitt y DLBCL. La translocación de MYC se asocia a mal pronóstico y escasa respuesta a terapias con R-CHOP, especialmente en casos que también presentan sobreexpresión de BCL2.
La expresión inmunohistoquímica de proteína nuclear en más del 70% de células tumorales es indicativa de la presencia de reordenamiento con alta sensibilidad y especificidad, por lo que resulta útil como test de cribado.
BIBLIOGRAFÍA
- Aukema, SM, et al. Double-hit B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2011;117:2319-31.
- Molyneux E M et al. Burkitt’s lymphoma. The Lancet 2012;379:1234-44
- Green, TM, et al. High levels of nuclear MYC protein predict the presence of MYC rearrangement in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:612-9.
- Johnson NA, Slack GW, Savage KJ et al. Concurrent Expression of MYC and BCL2 in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated With Rituximab Plus Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine, and Prednisone. J Clin Oncol 2012;30:3452-9.
- Muñoz-Mármol A et al. MYC status determination in aggressive B-cell lymphoma: the impact of FISH probe selection. Histopathology 2013;63:418-24.
- Shaoying L et al. MYC/BCL2 Double-Hit High-Grade B-Cell lymphoma. Adv Anat Pathol 2013;20:315-26.
- Thieblemont C and Brière J. MYC, BCL2, BCL6 in DLBCL: impact for clinics in the future? Blood 2013;21(12):2165-6.
- Cook JR, Goldman B, Raymond MS, Tubbs RR, Rimsza L, Leblanc M, Stiff P, and Fisher R. Clinical Significance of MYC Expression and/or “High-grade” Morphology in Non-Burkitt, Diffuse Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas. A SWOG S9704 Correlative Study. Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:494–501.
06/2014/ Montse Verdú